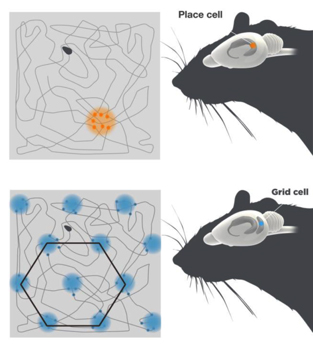
“Applied Evolutionary Psychology
S. Craig Roberts (ed.)
Print ISBN-13: 9780199586073
Published to Oxford Scholarship Online: January 2012
Chapter 8 – The evolutionary psychology of mass politics
Michael Bang Petersen
https://www.oxfordscholarship.com/view/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199586073.001.0001/acprof-9780199586073-chapter-0008

A number of modern political issues mimic ancestral problems of social living. By implication, our evolved social psychology is engaged by mass politics and helps facilitate the formation of public opinion and behaviour. Yet, the contextual differences between ancestral small-scale interaction and mass politics are many in terms of scale. On the one hand, the automatic operations of our evolved psychology prompt individuals to disregard these differences: individuals effectively think about mass political issues as small-scale social problems. On other hand, in the large-scale setting of mass politics, individuals cannot rely on directly available cues but are left with cues provided by media and political elites or, when these too are absent, on internally-generated cues. In these situations, our evolved social psychology will not so much facilitate a clear choice as produce ambivalence and attitudinal inconsistencies.
Keywords: evolutionary politics, leadership, voting, social behaviour
***
“Whenever an individualturns on the television, picks up a newspaper, or browses the Internet, it is likely that he or she willbe confronted with the developments in national or international politics. In this chapter, I will investigate how lay individuals process these developments and form opinions on them using evolved decision-making mechanisms. As will be seen, ancestral life in small hunter/gatherer groups has selected for a suite of mechanisms that are engaged by mass politics, but at the sametime these mechanisms evolved to function within a radically different context. By implication, whenever a mass political problem engages the evolved mind, it seems to be psychologically reduced to a problem of small-scale interaction.
(…)
The political animal
As group-living animals, a range of social problems such as sharing decisions, formation of collective action, punishment of free-riders, management of intergroup relations, and hierarchy formation would directly have impinged on the survival and reproduction of our ancestors (Buss 2005). The evidence supporting this assertion is overwhelming. Anthropologists have, for example, carefully compiled a list of human universals (i.e. traits that are present in all known human cultures). This list features inherently collective traits such collective identities, conflict, conflict mediation, cooperation, ethnocentrism, government, group living, law, leaders, property, sanctions for crime, and trade (Pinker 2002). Furthermore, the fossil record provides evidence that many of these activities are not only universal but have deep evolutionary roots. Hence, archaeological findings document that our ancestors have cared for the crippled and injured at least since 1.77 million years ago (Hublin 2009), have had elements of social organization at least since 750,000 years ago (Alperson-Afil et al. 2009), have hunted cooperatively and shared meat within groups at least since 400,000 years ago (Stiner et al . 2009), and have used weapons to engage inconspecific aggression since at least the Middle Palaeolithic (Walker 2001).
(…)
These insights from evolutionary psychology are important for our understanding of political behaviour because ancestral problems related to social living carry structural similarities to modern political problems such as welfare, tax payments, criminal sanctions, immigration, warfare, race relations, and redistribution (Alford and Hibbing 2004; Schreiber 2006; Petersen 2009). Both sets of problems are, essentially, about distributions of costs and benefits within and between groups. By implication it is plausible that, during normal development, the human mind builds a tool box of mental programs directly applicable to the issues of mass politics. This toolbox should facilitate the formation of political attitudes and the execution of political decisions.
To the evolved mind, all politics is local
Our social decision-making apparatus was designed by natural selection to produce decisions that would constitute adaptive ‘best bets’ in the particular environment in which it evolved (Toobyand Cosmides 1992). In this respect, it is notable and important that modern politics is played out in large-scale nation states comprising millions of individuals, because large-scale societies are extremely recent evolutionary phenomena. States first emerged in the world around 5000 before present (BP) and, while state technology rapidly diffused to some parts of the world, states inother parts of the world were only formed within the last centuries (Petersen and Skaaning 2010).For millions of years prior to that, human evolved as hunters and gatherers in small-scale groups with between 25 and 200 individuals (Kelly 1995). Most parts of our species-typical social decision-making apparatus are, in other words, designed to be operative within the causal structure of a small-scale social environment rather than a large-scale mass society. This implies, first,that the input this apparatus is designed to extract and process from decision-making contexts would be cues causally relevant for adaptive choice in small-scale interaction and, second, that the cognitive and motivational output this apparatus produces is that which would solve a given problem in a small-scale context.
We have no reason to believe that modern individuals should be particularly aware of these built-in assumptions and, hence, they may not be able to correct for them. Rather, prior research in other fields suggests that evolved decision-rules operate in an automated fashion. This has important consequences (Price 2008), for example, argues that because of their automated nature, evolved decision-rules are switched on by any cues that mimic ancestrally recurrent cues even when these are present in a novel situation and, upon triggering, cause individuals to misapprehend the novel situation as a related evolutionarily recurrent one (see also Hagen andHammerstein 2006).
(…)
to the extent that individuals’ attitudes on modern political issues are formed using evolved decision making mechanisms, these attitudes will implicitly assume that mass politics are in fact played outin a local small-scale setting. In other words, to paraphrase an often heard expression about politics: to the evolved mind, all politics is local. The information that people find intuitively relevant when producing political choices will be information of relevance in small-scale social environments; and the political solutions that people will find intuitively correct will be solutions that work within such environments. This effect, it must be stressed, does not arise because modern individuals are not consciously aware that the problems of state-centred politics are different from the problems they encounter in local settings with, for example, their wife, friends, neighbours, and colleagues. Rather, it is because the automatic operations of evolved decision-rulesswamp the opinion formation process of individuals and make the differences seem irrelevant and uninteresting.
(…)
individuals think about mass politics in terms of ancestral small-scale interaction–whether or not this is rational from a modern-day perspective. Hence, males react as if disputesover national policies were a matter of direct physical confrontation among small numbers of individuals, rather than abstract electoral dynamics among millions.
(…)
Ancestral coalitional conflict and political groups
(…)
Our evolved coalitional machinery should be activated in all contexts containing cues that ancestrally would have disclosed the existence of group-based cooperation and conflict. In modern politics, one such context is conflict between political parties. Political parties are characterized by high levels of within-party cooperation and between-party conflict. By implication then, some of the above mechanisms should also take effect in modern party politics. In one study, affiliations with a political party were found to be psychologically represented as coalitional affiliations — atleast for males. Stanton et al. (2009) followed party supporters on the night of the 2007 US presidential elections, measuring their testosterone levels. Studies of humans and other animals have demonstrated that male testosterone levels fall in response to losing status, presumably to motivatea de-escalation of conflict. The same hormonal pattern was observed among supporters of the Republican party immediately after Barack Obama, the Democratic candidate, was announced as the winner. Having voted for the losing party felt just like losing a direct status competition.
Another study focused on the notion that, if political affiliation is conceptualized as a coalitional identity, political attitudes can come to serve as coalitional badges (Petersen et al. in prep.). That is, individuals can come to have certain attitudes to signal that they are loyal partisans. If parties change position on an issue, voters usually do not shift allegiance to another party but rather change their position too (e.g. Goren 2005; Zaller 1992). In support of an evolutionary interpretation of these effects, Petersen et al. (in prep.) identified sex differences in the way citizens’ attitudes are used as coalitional badges. Subjects were primed with demeaning statements about a party attributed to a spokesman from another party. After priming, they were asked about their opinion on a policy proposal that was either attributed to the attacked party or the attacking party (keeping the content of the proposal constant) and, hence, were provided withan opportunity for signalling coalitional loyalty. As expected, males reacted in a highly coalitional manner to the primes. When their preferred party was attacked in the statement, they became more willing to support policy when attributed to their party, and less willing to support it when it was attributed to the other party. Females, however, reacted in a conciliatory fashion. When their preferred party was attacked by another party, they become more willing to accept the policy proposal by this other party, as if to appease the attacker. Female appeasement strategies have been observed among females in small-scale conflict situations (Salter et al. 2005) and make evolutionary sense in this context given the lack of female physical strength. In modern party politics, however, there seems to be less, if any, rational reason to back off in this manner.
The anonymity of mass politics and processing implications
The above examples illustrate situations where modern humans misapprehend political issues as ancestral adaptive problems. From this, one obvious expectation would be that people intuitively find politics interesting and engaging. After all, the argument implies that politics is implicitly represented as about matters of survival and reproduction. While there is certainly truth to this, it is, however, not the whole truth. The human political animal is, in fact, one with a paradoxically low interest in day-to-day affairs of modern politics. Since the first studies of public opinion and voting behaviour, political scientists have repeatedly documented how little citizens know, think, and care about politics (e.g. Converse 1964; Zaller 1992). Specifically, researchers have demonstrated that citizens do not know basic facts concerning their political system, such as the numberof seats in the legislature or the identity of those holding specific office (Carpini and Keeter 1996).Furthermore, a number of studies have demonstrated that a large number of people find it difficult to decide on political issues. On issues such as abortion and criminal justice, the public are ambivalent and most see merits in the arguments of both sides (Craig and Martinez 2005). Finally, a large number of studies have revealed that citizens have difficulties in sticking to their principles. Even though individuals in general support freedom of speech for everybody, they are often quite willing to limit the freedoms of specific groups (McClosky and Brill 1983). Similarly, individuals who support harsh punishments for crimes can be quite lenient towards specific criminals (Roberts 1992).
Any attempt to apply evolutionary psychology to the study of modern political attitudes and behaviour needs to reconcile the conclusion from evolutionary biology that humans are political animals with these observations from political science. If humans were endowed with a natural sense of politics, would citizens not think of mass politics as an interesting and intuitive affair?
Processing without cues
One reason that this turns out not to be the case is that some modern issues bear little relation ship to recurrent adaptive problems and, hence, do not activate natural intuitions. Technological advances in modern society have spawned a range of new issues (e.g. regulation of the macroeconomy). From the perspective of evolutionary psychology, such novel issues that do not fit evolved decision-mechanisms should indeed appear uninteresting and difficult to grasp. Yet, the technological advances of modern societies are insufficient to explain the lack of political attention among modern citizens. In addition, one needs — again — to focus on the contextual differences between modern mass politics and ancestral social interaction. Hence, the key to understanding how a political animal can be quite politically inattentive lies in the fact that our social decision-making mechanisms evolved in information-dense situations characterized by repeated face-to-face interactions. By implication, to disclose and solve adaptive problems of social life, our decision-making mechanisms are designed to rely on intimate social cues such asfacial expressions, knowledge of past interactions, and so on.
In the context of mass politics, these myriad subtle cues will often be lacking. Given that modern politics is played out in large-scale nation states comprising millions of individuals, the majority of citizens do not know and will never meet each other, and most often, citizens are required to form opinions and impressions of anonymous strangers. Modern politics, in other words, is characterized by information scarcity and our decision-making apparatus is unable to extract the detailed information necessary for its execution.”